Challenges to the Transformation of Enterprise WAN
Branch Office Connectivity Challenges
Connecting branch offices has been a significant challenge for geographically-dispersed multinational enterprises; 73% of companies surveyed have reported that the connection of branch offices is an important issue for business.
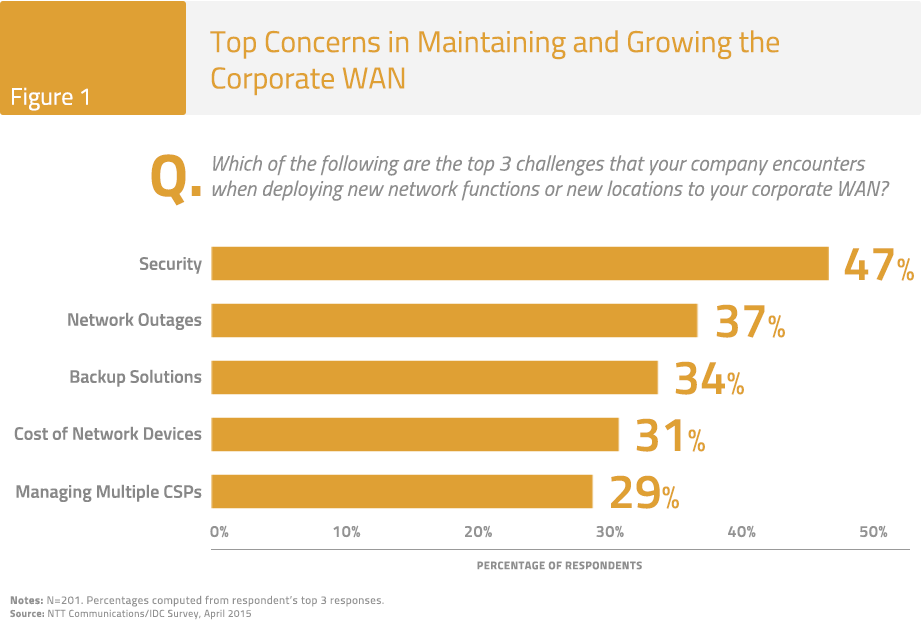
There are several key issues impacting the ability of enterprises to successfully implement and manage branch connectivity. The primary concern is still security, followed by network reliability and the impact of network outages, providing timely and cost effective on-site support and data back-up solutions. The chart below (Figure 1) shows a ranking of the top issues in maintaining the enterprise WAN.
For example, enterprises are using cost-effective Internet to connect smaller branch offices and/or remote workers from several different communication service providers (CSPs) and tunneling the traffic to their WAN CSP. This could often lead to data breaches, degradation of performance and operational complexity. Some enterprises are also implementing hybrid VPN solutions (using Internet access to aggregate and then connect traffic to the MPLS VPN) or using Internet-based VPNs, which can both address part of the security challenges, but may not always meet performance or application SLAs.

Virtualization of the Branch Office
Another emerging enterprise requirement is for cloud-based delivery of WAN services to any branch office which results in a reduction the number of physical network CPE appliances at each site. The virtualization of network appliances reduces the complexity and cost associated with managing separate, dedicated hardware-based firewall, router, and DDoS mitigation by incorporating these intelligent services in a secure virtualized cloud that is delivered to a lower function CPE router that supports software-based WAN services. Nearly one-third of managers surveyed cited the cost of network devices as a top concern in their efforts to grow the corporate WAN.

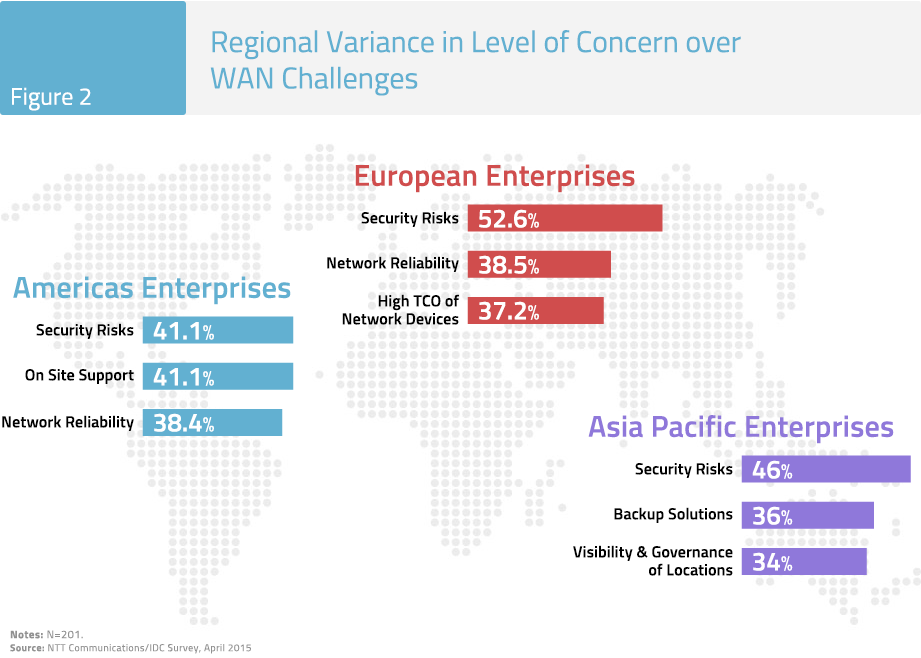
Looking by region, security remains the number one issue in all regions, but on-site support is of particular importance in the Americas (see Figure 2).

Over the last five years, WAN technologies for managing branch locations have evolved and grown in complexity. IT managers have to manage multiple architecture types including Layer 2, or Layer 3 VPNs, multiple access and storage platforms as well the exponential growth of mobile devices and operating platforms.
As a result of this complexity, IT managers have steadily moved to outsourcing the management of branch offices and their WANs. Complex technology platforms, multiple national regulations and compliance regimes bring added costs in managing multinational operations. Migrating management to a CSP can provide multiple benefits by allowing enterprises to focus on their primary business rather than managing IT staff in multiple countries.

Consistent User Experience for Mobile Users
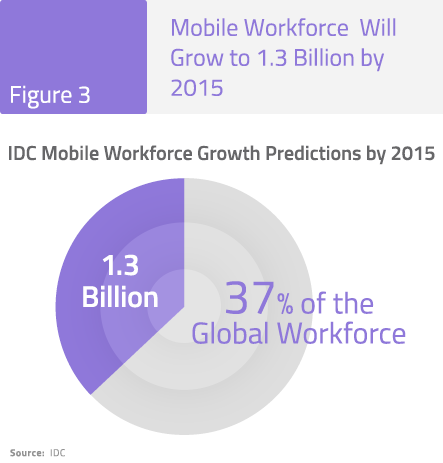
In today’s fast-changing technology and competitive environment, IT must find ways to balance short-term demands with long-term needs. While both cloud and mobility are creating new opportunities, they also bring new challenges. Wireless projects are frequently funded by line of business managers and can include decentralized purchasing of services and devices or the installation of WiFi hotspots as well as unauthorized corporate access from mobile devices.
Implementing a centralized global, consistent mobile policy ensures both security and a high user experience standard. While mobile services can be a challenge to manage for multi-national corporations (MNCs) with geographically dispersed sites and employees, enterprises can implement solutions that will facilitate consistency and secure access and experience. Implementing consistent managed LAN and access polices and for mobile device authentication are important issues for IT managers.

Flexible and Secure Access for Partners
Facilitating partner connectivity has emerged as a very important aspect of enterprise networking. An effective supply chain is essential to success and implementing a reliable and secure networking relationship is crucial to the execution of mission critical applications.
Partner networking is very similar to branch networking. Depending on the level of traffic and type of applications in use, partner connectivity can range from point-to-point dedicated circuits, broadband connectivity for occasional data exchange to highly secure Ethernet and MPLS VPN connectivity. As in the provision of branch connectivity, enterprises require a reliable, secure networking environment that will span many protocols and platforms. This requires a CSP that has the global coverage and experience to manage any-to-any connectivity effectively.
Performance of Cloud Applications Relies on Secure, Highly Available Connectivity
The next decade will see enterprises employ a wide range of commercial software, cloud, and mobile IP–based applications, raising the importance of robust WAN IP connectivity solutions that will include the use of more on-demand network resources. Enterprises are evaluating and adopting hosted or cloud WAN solutions for selected applications such as VoIP, UC, storage, computing and video. The cloud WAN solution can be either private (on-premise) or public (hosted offsite). Normally, hosted services imply that a fixed set of compute resources are made available.
The economic appeal of cloud (elasticity, pay as you use, self-service) resonates with both in-house and third-party hosting enterprises. As more and more applications are moved to the cloud and shared with remote branch offices, partners and roaming employees, enterprises are migrating from legacy fixed bandwidth to higher and more flexible on-demand bandwidth options, including SLAs that may cover installation, repair, network availability, network latency, and packet loss.

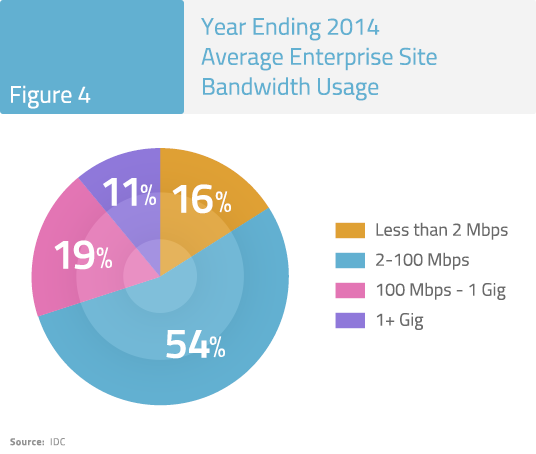
By the end of 2015, IDC expects that enterprise bandwidth usage will increase substantially, with 100-500 Mbps and Gigabit segments showing the fastest growth.
